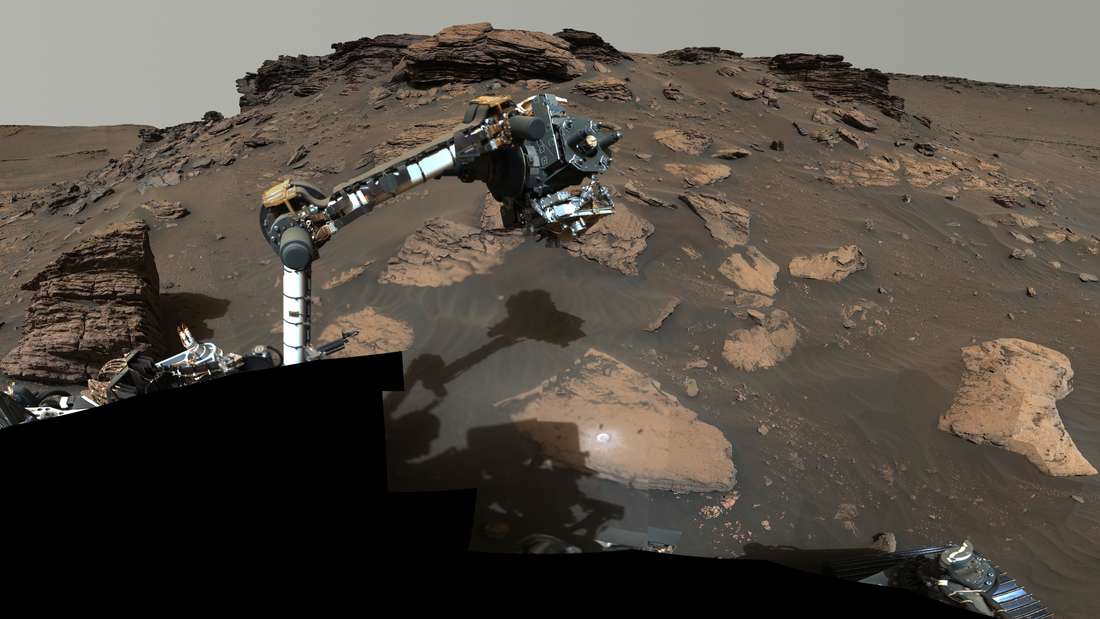
NASA’s Perseverance rover makes an important discovery in the river delta on Mars. But now researchers will have to be patient for a long time.
Pasadena – as the US Space Agency NASA As the landing site for an area called Jezero Crater persistence rover Feather Mars planet The selected, responsible people already had a plan: They wanted to use robots to trace an area that looked like a river delta on images already taken by the space probe. “Perseverance” has been exploring the delta since July 2022 – and is now providing particularly important samples.
“We chose Jezero Crater for the exploration of Perseverance because we thought it had the best chance of obtaining scientifically outstanding samples,” said NASA science director Thomas Zurbuchen. “Now we know we’ve sent the rover to the right place.” The Mars rover collected an “incredible variety of samples” that will be brought back to Earth by another Mars mission in the future. “I think it’s safe to say that these are the two most important samples we’re going to collect on this mission,” said David Shuster, who is responsible for getting the samples from Mars.
NASA’s Perseverance rover finds organic material on Mars
The delta in which the Mars rover Perseverance is located was formed about 3.5 billion years ago. It marks the place where in the past a river Mars flowed into a lake. The Persistence rover is currently studying sedimentary rocks in the delta, when particles of various sizes once settled in a wet environment. “The rocks we examined have the highest concentration of organic material ever detected during the mission,” said Perseverance project scientist Ken Farley at a NASA press conference. “Organic molecules are the building blocks of life, so it is very interesting that we have rocks deposited in a lake in a habitable environment that contain organic material.”
According to NASA, the “persistence” instrument SHERLOC already took a sample on July 20, in which researchers found a class of organic molecules related to sulfate minerals. Sulfate minerals found in sedimentary rocks can provide important information about the aquatic environment in which they formed. “This relationship suggests that both sulfate and organic matter were deposited, preserved and concentrated in this area during the evaporation of the lake,” explains Sherlock scientist Sunanda Sharma. “Personally, I find these results so dynamic because I think we’re in the right place at a very crucial time and with the right tools.”

Mars: Organic molecules once found in habitable zone
NASA uses the term “organic molecule” to describe a large number of compounds that primarily contain carbon and usually hydrogen and oxygen atoms. It may also contain other elements such as nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus. However, there are also chemical processes in which such molecules are formed without the involvement of biological life – such a discovery does not necessarily indicate earlier life on Mars. In fact, “persistence” and its antecedents, Curiosity Rover already Organic matter found on Mars, But the fact that it was found this time in an area showing that there was liquid water in the past, and which may have been habitable, is an important clue for researchers.
The rocks we examined have the highest concentration of organic material ever detected during the mission.
Sharma explains, “While the detection of this class of organic matter alone does not mean that there was definitely life, these observations are somewhat similar to what we have observed here on Earth.” “To put it simply, if this is a treasure hunt for possible signs of life on another planet, organic matter is a lead. And as we move through the delta, we get stronger and stronger clues .
NASA and Esa want to take soil samples from Mars to Earth
After such significant discoveries, scientists would like to immediately go to work and examine the material in detail. However, researchers will have to be patient for some time before they can conduct detailed research on the organic material found. “As capable as our instruments on Perseverance are, further conclusions about the material of the sample will have to wait to return to Earth,” says Farley.
space newspaper
What will science discover next on Mars? And why hasn’t anyone landed there yet? Of free space newsletter Keeps you updated twice a month.
so called Mars sample return missionwith NASA European Space Agency Collaborates, is said to have “persuasively” collected samples of Mars. Assemble two small helicopters using drones and bring it back to Earth – but as of the 2030s, an exact date has yet to be determined. (tab)

Web guru. Amateur thinker. Unapologetic problem solver. Zombie expert. Hipster-friendly travel geek. Social mediaholic.