In the bustling world of manufacturing and production, the role of industrial robots has become increasingly indispensable. With their precision and efficiency, these mechanical marvels have revolutionized various industries, enhancing productivity and quality while reducing costs. As we delve into industrial robotics, we encounter various machines designed to cater to specific tasks and environments.
Understanding Industrial Robot Types
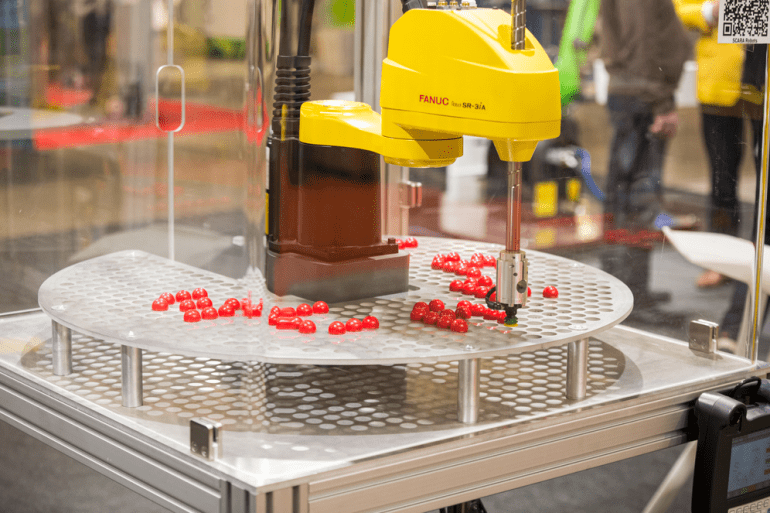
SCARA Robots
SCARA robots, an abbreviation for Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm, are identified by their inflexible vertical arm and flexible horizontal arm. This configuration enables them to execute operations swiftly and accurately, rendering them well-suited for assembly, pick-and-place tasks, and packaging within the electronics and automotive manufacturing sectors.
Delta Robots
Delta or parallel robots are characterized by three arms linked to a shared base. They thrive in environments demanding swift and precise movements, such as food packaging, pharmaceuticals, and electronics assembly. Their distinctive kinematic configuration facilitates rapid motion and increased throughput, making them a preferred choice for industries with high-speed production requirements.
Cartesian Robots
Cartesian robots, called gantry robots, utilize a Cartesian coordinate system for motion control. Their linear movement along three orthogonal axes makes them well-suited for applications requiring precise linear motion, such as material handling, machining, and 3D printing. Cartesian robots offer simplicity and robustness, making them versatile solutions for various industrial tasks.
Articulated Robots
Articulated robots mimic the structure of the human arm with multiple joints, enabling them to maneuver in complex, three-dimensional spaces. These robots find applications in welding, painting, and material handling across automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery industries. Their dexterity and range of motion make them indispensable for tasks requiring intricate manipulation and flexibility.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Collaborative robots, commonly called cobots, are engineered to operate alongside humans in a shared workspace without compromising safety. Unlike conventional industrial robots, cobots have sophisticated sensors and safety features that enable them to detect and react to human presence, reducing the likelihood of accidents and injuries. Cobots are utilized across various industries, including healthcare, logistics, electronics assembly, and small-scale manufacturing.
Comparative Analysis of Industrial Robot Types
In comparing industrial robot types, several key factors come into play:
Performance Metrics
Each type of industrial robot possesses unique performance characteristics, including speed, payload capacity, and repeatability. SCARA and delta robots, for instance, excel in high-speed applications, while articulated robots offer greater flexibility and maneuverability.
Flexibility and Versatility
Industrial robots’ flexibility refers to their ability to adapt to diverse tasks and environments. With their linear motion capabilities, Cartesian robots offer versatility in handling various payloads and workpieces, making them suitable for various applications.
Accuracy and Precision
Precision is paramount in industries requiring tight tolerances and quality control standards. SCARA and delta robots, known for their precise positioning capabilities, are often employed in applications demanding high levels of accuracy, such as microelectronics assembly and medical device manufacturing.
Cost-effectiveness
The initial investment cost and the total cost of ownership vary across different types of robots. While SCARA and Cartesian robots are generally more affordable and easier to integrate, articulated and delta robots may offer higher performance but at a higher price point.
Safety Features
In an era of increasing human-robot collaboration, safety is of paramount importance. Collaborative robots are equipped with advanced safety features, such as force sensing and speed limitation, to ensure the well-being of human operators working alongside them.
Emerging Trends and Innovations in Industrial Robotics
The landscape of industrial robotics is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and market demands. Some notable trends and innovations include:
Sensory Technologies
Advancements in sensory technologies, including vision systems, LiDAR, and tactile sensors, equip industrial robots with enhanced perception capabilities. These sensors enable robots to perceive and interact with their surroundings more intelligently, facilitating task recognition, quality inspection, and obstacle avoidance.
Enhanced Programming Capabilities
The emergence of intuitive programming interfaces and offline simulation tools simplifies the programming and deployment of industrial robots. User-friendly interfaces allow operators with varying levels of expertise to program and reconfigure robots quickly, reducing downtime and increasing operational flexibility.
Human-Robot Collaboration Advancements
Collaborative robots continue to evolve with improved safety features and intuitive interfaces that promote seamless interaction between humans and machines. As collaborative applications expand across industries, advancements in human-robot interaction enable safer and more efficient collaboration in shared workspaces.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Industrial Robots
While industrial robots offer numerous benefits, their implementation poses several challenges and considerations:
Initial Investment Costs
The upfront cost of acquiring and integrating industrial robots can be substantial, requiring careful financial planning and justification.
Maintenance and Support Requirements
Industrial robots require regular maintenance and support to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This includes preventive maintenance, troubleshooting, and access to spare parts and technical support.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating industrial robots into existing production systems can be complex and time-consuming, requiring compatibility with existing machinery, processes, and software.
Workforce Adaptation and Training Needs
Adopting industrial robots may necessitate workforce training and re-skilling to operate and maintain these sophisticated machines effectively.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Compliance with industry regulations and safety standards is crucial to ensure the safe operation of industrial robots and mitigate potential risks to human operators and the surrounding environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the diverse landscape of industrial robots offers many solutions to meet the evolving needs of modern manufacturing and production environments. From SCARA and delta robots to collaborative cobots, each type of industrial robot brings unique capabilities and advantages. As technology advances and industries embrace automation, the journey towards greater efficiency, productivity, and innovation in industrial robotics is poised to redefine the future of manufacturing and beyond.

Introvert. Proud beer specialist. Coffee geek. Typical thinker. Pop culture trailblazer. Music practitioner. Explorer.