fuerote gas cloud
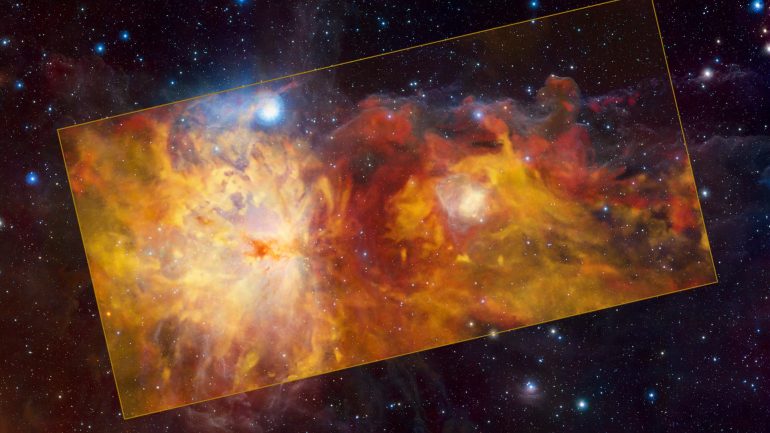
The Orion cloud is blazing, but the gas composition certainly isn’t igniting. Rather, from 1,300 to 1,600 light-years away from Earth, there are new planets and stars whose radiation causes the gas in their atmosphere to glow. The image in the rectangle, which shows the so-called Flame Nebula and its surroundings, was taken at the European Southern Observatory (ESO). A team led by ESO astronomer Thomas Stanke in Garching used the SuperCAM instrument on the Atacama Pathfinder Experiment (APEX) radio telescope in Chile in 2014. However, the results recently emerged In the journal “Astronomy and Astrophysics”,
The research team imaged the Flame Nebula and its surroundings from radio waves released by carbon monoxide in the Orion cloud. The different colors indicate how fast the gas is moving in the Orion Cloud. Basically the structure moves away from us. Dark red areas are brighter than light yellow areas. Contrary to what the colors used might suggest, the gas clouds are not hot, but extremely cold. There it is likely to be just a few tens of degrees above absolute zero, which is −273.15 °C.

Web guru. Amateur thinker. Unapologetic problem solver. Zombie expert. Hipster-friendly travel geek. Social mediaholic.