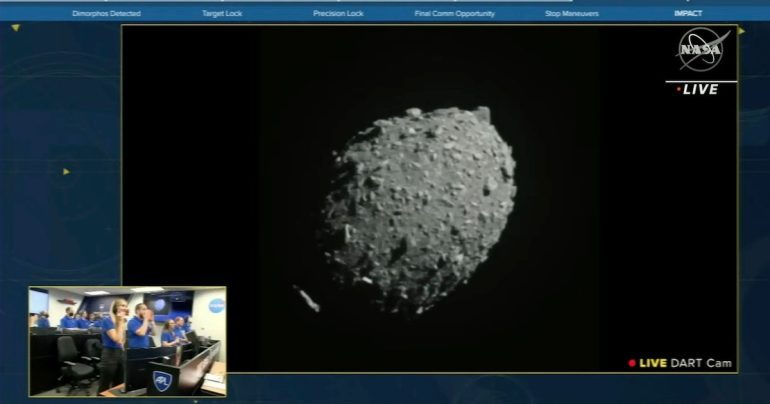
first intentional collision of a spacecraft With an asteroid, according to the first video of the maneuver, there was a great impact. The grainy black-and-white images show first the asteroid moon Dimorphos, and then a giant cloud of debris and dust ahead of Dimorphos. This indicates that the NASA probe Dart severely impacted the celestial body as desired.
“We have found damage to dimorphos,” said Patrick Mitchell of the European Space Agency (ESA), who is involved in explaining the experiment. The amount of “removed material” is “quite unbelievable”. can be used to estimate the surface density of
Asteroid Damaged: Probe Dart Is About the Size of a Car
US space agency NASA last year sent the Dart space probe into space so that it could collide with the asteroid moon Dimorphos and change its orbit. On Tuesday night, the probe, which was about the size of a car, then moved into the celestial body at more than 23,000 kilometers per hour.
It was the first ever maneuver in space that tested the defense against an Earth-threatening asteroid. Its purpose was to slightly alter Dimorphos’ orbit around the asteroid Didymos and to shorten its orbital period from the previous twelve hours to ten minutes.
To drive a dangerous asteroid over Earth in an emergency, only minimal course change would be necessary with early intervention. Similar technology was previously known only from science fiction films such as “Armageddon”.
Probe Dart Produces “Very, Very Large” Dust Cloud
The ATLAS Asteroid Alert System released video of the maneuver made from images from its telescope in South Africa. According to Atlas scientist Larry Deneu, the telescope took a picture every 40 seconds. The resulting video therefore shows a two-hour period in time lapse.
Danue reported that the Dart probe produced “very, very large” clouds of dust upon impact. Its diameter was several thousand kilometers.
The analysis of the Dart experiment will continue in the coming weeks. For an even more detailed investigation, ESA wants to send its Hera probe in 2024, which should reach the asteroid two years later. The German Aerospace Center (DLR) is significantly involved in the mission.


Internet fan. Alcohol expert. Beer ninja. Organizer. Certified tv specialist. Explorer. Social media nerd.