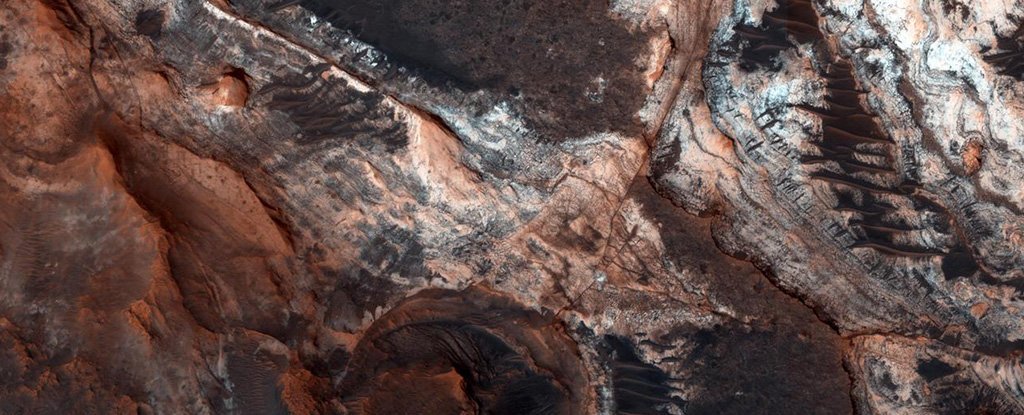
The problem of whether or not historical lifestyle could have existed on Mars centres on the h2o that the moment flowed there, but new investigation revealed Monday implies that several of the Purple Planet’s valleys ended up gouged by icy glaciers not rivers.
The research in Character Geoscience, which will come amid a flurry of new Mars missions trying to find out if the now-barren earth ever hosted existence, casts question on a dominant idea that the planet as soon as experienced a heat, soaked local climate with considerable liquid drinking water that sculpted the landscape.
Researchers from Canada and the United States examined additional than 10,000 Martian valleys and as opposed them to channels on Earth that were carved beneath glaciers.
“For the very last 40 a long time, since Mars’s valleys have been to start with discovered, the assumption was that rivers the moment flowed on Mars, eroding and originating all of these valleys,” claimed direct creator Anna Grau Galofre in a statement launched by the University of British Columbia.
But these formations occur in a massive variety “suggesting that numerous processes were at enjoy to carve them,” she added.
Scientists located similarities amongst some Martian valleys and the subglacial channels of Devon Island, in the Canadian Arctic, which has been nicknamed “Mars on Earth” for its barren, freezing ailments and hosted NASA place education missions.

Previously mentioned: Collage demonstrating Mars’s Maumee valleys (top rated fifty percent) superimposed with channels on Devon Island in Nunavut (base 50 %). The condition of the channels, as effectively as the in general community, appears almost equivalent.
The examine authors stated their findings propose that some Martian valleys could have been formed some 3.8 billion many years back by meltwater beneath ice sheets, which they said would align with local climate modelling predicting that the planet would have been significantly cooler in its historic previous.
“The conclusions display that only a fraction of valley networks match patterns common of area drinking water erosion, which is in marked contrast to the standard watch,” stated co-creator Mark Jellinek.
Nature Geoscience mentioned that knowledge local weather disorders “in the very first billion many years of Mars’ background is significant in identifying no matter if the earth was at any time habitable”.
The review authors claimed that icy temperatures could in simple fact have better supported historical everyday living.
“A sheet of ice would lend additional protection and stability of underlying water, as properly as providing shelter from photo voltaic radiation in the absence of a magnetic industry – anything Mars once experienced, but which disappeared billions of several years ago,” the University of British Columbia assertion claimed.
The research comes right after NASA released its newest Mars rover, Perseverance, to glance for signs of historical microbial daily life on the Pink World.
If all goes to program, Perseverance will get to Mars on 18 February 2021 and gather rock samples that could deliver invaluable clues about no matter whether there was ever past daily life on Mars.
However, the retrieval and assessment is not anticipated prior to the 2030s.
China has also released its very first Mars rover, which need to arrive by May possibly 2021.
© Agence France-Presse

Pop culture practitioner. Bacon expert. Explorer. Tv maven. Wannabe student. Subtly charming social media nerd.